Understanding Packet switching
Does Your data packet follows a single path during transmission?
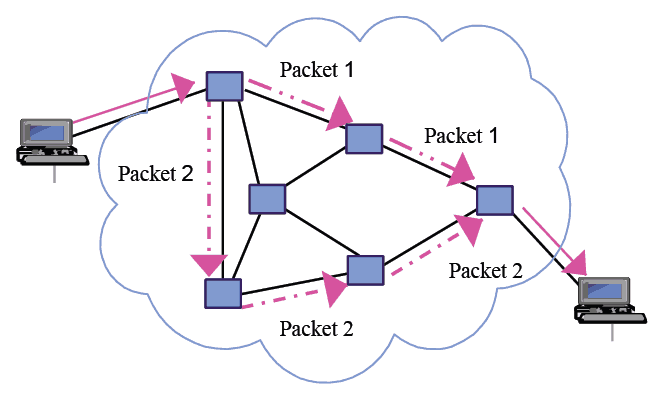
The data in data communication is sent in the form of chunks that are called data packets. i.e. sender sends data in the form of data packets and receiver receives it in the same form. The transmission of those data packets in between those two ends is a quite interesting part in the communication model.
There are many more routes present between the two ends. Now the data has got two options. First to follow a single path and other that each data packet will follow different path according to their choice. Here comes the idea of switching.
Switching is process to forward packets coming in from one port to port leading towards destination. And it is mainly done in two ways. Circuit switching and Packet switching.
If we try to understand both of these terms, let’s take an analogous example of road transport. Where vehicles are the data packets, the toll stations as intermediate router. Now every vehicle is free to choose its own path to reach to the destination (packet switching) whereas if any VVIP person goes from the source to destination, all the vehicles move in a queue along a single previously fixed road(circuit switching).
Now, we will dive deeper into packet switching as it is the widely used technique in these days. And try to understand it using different constraints and aspects.
◼ Delay- This technique does not need connection to establish and then begin data transfer. Data transfer starts as soon as the packets are thrown on the network. The delay in packet switching is not uniform as it depends on the traffic, bandwidth etc.
The every intermediate router in the path takes some time to process and decide the path of the packet which is often termed as processing delay.
One more factor which causes the delay is the unlikeness in the receiving and sending rate at the router. i.e. if router’s sending rate is much more larger than the sending rate of the previous router. Then the router has to wait for the packets to come which adds delay in the transmission.
What if the case is different? The packets are coming at greater speed but the router doesn’t have capacity to handle all of them at a time. The router have to make them wait until the present packets are transmitted further by putting all of them into queue. This causes queuing delay.
◼ Reliability- Packet switching is less reliable than the other transmission techniques. In this method, transmission of data is not only done by the sender but by the intermediate routers also. They also play a crucial role in determining the path for the data packet depending on traffic, routing capacity etc. In other words, it is store and forward technique so considered to be less reliable.
◼ Data transmission- The data transmission begins as soon as the data is placed over the network. The data packets follow various paths to reach to the destination. In order to combine the data packets again in the original data, OS gives each packet a sequence no. And they are again merged on the basis of this sequence.
◼ Error Handling- A question comes in mind what if any of the packet is not received at the receivers end or any error is caused? In this case receiver demands for the missing data packet again. And retransmission of the data packet takes place. The circuit switching doesn’t provide this flexibility. Either your data will be completely reached or completely lost in between.
◼ Network performance- The term refers to measures of service of a network as observed by the customer. Packet switching is an efficient technique. It doesn’t require any established path prior to the transmission, and many users can use the same communication channel simultaneously, hence makes use of available bandwidth very efficiently and gives good rate of data transfer.
Now a question arises,
Does internet uses packet switching as a default transmission technique? Is there any advanced option available to communicate data on internet.
In most of the data transmissions in the world today uses packet switching. With advancement in the field of networking and growing web of routers and internet, many more path are available now in between source and destination. The data packet has got more no. of options to choose the path it wanted to travel.
But with passage of time and necessity more advancement in this field has taken place which have made the data transmission more reliable.
MPLS (Multi Protocol label switching) is one of them.
It is a mechanism for routing traffic within a telecommunication network, as data travels from one network node to the next. In an MPLS enabled network, MPLS does label switching which means the first router or network device does a routing lookup, but instead o finding a next hop, it finds final destination router.
Working of MPLS-
In MPLS, packets are directed through the network based on an assigned label. A label is a short, four-byte, fixed length, locally significant identifier. The label is associated with predetermined path through network, which allows higher level of control than in packet switched networks.
With pure IP (Internet Protocol) routing in a packet switched network, each data packet could determine its own path through the network which has dynamic flow, but not predictable. And however it is very cost effective.
In previous circuit switched networks, physical wires and telephone lines carried data and voice traffic. That provided predictable routes, but was very expensive and difficult to scale because of the need to put in extensive infrastructure.
So MPLS have evolved to allow control of network routing, creating paths that act like a point to point connection within a network, but are virtual and flexible instead of physical.
MPLS has no physical circuits, but virtual circuits.
Label Switching in MPLS routing-
The packet enters the edge of the MPLS backbone, is examined, classified and given an appropriate label, and forwarded to the next hop in the pre set label switched path (LSP). As the packet travels that path each router on the path uses the label and not other information. Such as the IP header to make the forwarding decision that keeps the packet moving along the label switched path.
However, Within each router, the incoming router is examined and its next hop is matched with a new label. The old label is replaced with new label for the packet’s new destination, and then freshly labelled packet is sent to the next router. Each router repeats the process until the packets reaches the last router.
The label information is removed at either the last hop or the exit router, so that the packet goes back to being identified by an IP header instead of an MPLS label.
MPLS is a simple, secure telecommunications solution. Because you do not have to deal with encryption or special hardware, MPLS can serve as the backbone of cost-effective, secure communications. Moreover MPLS is a flexible network solution that allows companies to scale and customise their solutions.
When compared to all the other routing techniques available MPLS is still the fastest data carrying technique available.
Let us understand the mechanism by using an example-
Sender present in the lower left location wants to send message to receiver present at the upper right corner.

The message delivery takes place in the forward manner -
1.The sender have made a data packet and sent on the network line. Now the LER(Label Edge Router) Has established the connection. The LER checks for the destination address and Without changing the contents and header of the data packet one label is added (17) to the packet which is going to be considered for the further journey.
2.The packet has reached next router now. The LSR(Label Switch Router) checks label to be replaced in the table and the label is swapped with (24). Now the packet will start its new journey with new identity.
3.Once the packet is reached to the destined LER the label is removed and the packet is delivered in its original format.
